If are you facing a “No Root File System is a Defined error” then you are in the right place. The root file system is a site within the system where one mounts all other file systems when booting up the device, and it is to be located in the same partition where the root directory is situated.
Why No Root File System is Defined Error Occur
1. You will get the “No Root File System is defined” error whenever you try installing a Linux or Ubuntu distribution while utilizing a Windows partition (FAT32 or FAT).
2. The “No Root File System is defined error” might crop up even when one has not created a Linux partition.
3. This error will also occur when a Linux partition is not defined even though it could have existed.
Be careful to follow each step one at a time, and once your error is rectified, you can go ahead with your Linux or Ubuntu installation easily.
If you get this error, you need not worry but instead, must rectify it. Several ways in which the error can be rectified include the ones suggested below;
How To fix the “No Root File System is defined” Error
To fix the No Root File system is defined error, you have three ways, and you must follow the steps closely for each of the different fixes.
1. Make sure you have set a definition for your root partition
Even if you have a root partition but you missed defining it, you can even then get the “No Root File System is defined error.”
Usually, if you have not set a root mount point, you cannot have the mount point in the partitions. If you want to rectify this error, here is what you must do.
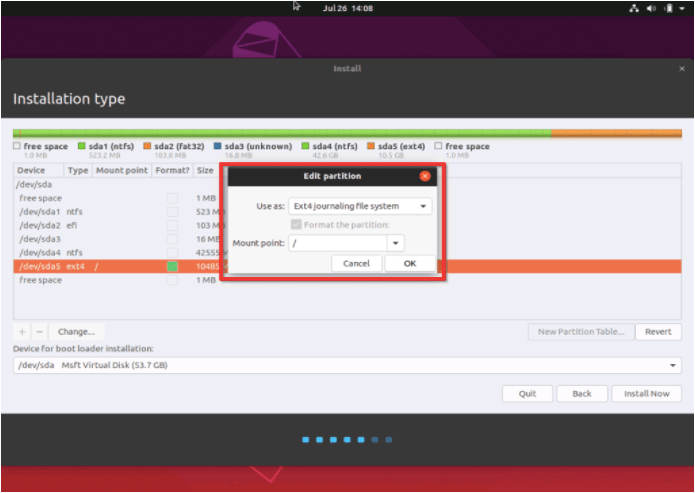
1. To rectify this error, you must right-click on the partition you want to utilize and then choose the Change option.
2. After choosing the partition, you must double-click on it.
3. Besides the Mount option, an edit partition option will open up.
4. Choose /. Before pressing the OK tab.
To find root file systems in Windows, here are the steps.
5. Press the Windows + R tabs and type “cmd” in the command prompt.
6. When the command window appears, type in “set systemroot” and press the Enter tab to open the system roots.
Once you have created a partition, you can now proceed with your Ubuntu or Linux installation. Choose the partition you have made and then check the Format column, and now you must click the Install tab.
2. Remove the current Windows partition
If you are trying to install Ubuntu or Linux installations in a FAT 32 or FAT partition and obtain the “No root file system is defined error,” you must then remove the partition. Once the partition is removed it will be blank and will appear as a free unit or partition.
You must create the partition again to continue with the installation process. But how do you create the partition again? Follow the steps given here to create a new partition for continuing with the installation process to prevent the ‘No root file system is defined error’ from occurring.
1. To remove a partition, you simply must select it, right-click on it, and then press the delete tab to remove it.
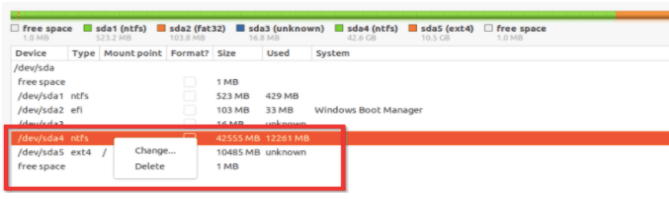
2. If you want to alter the file system, try doing that by choosing the Linux File System from the different file systems available.
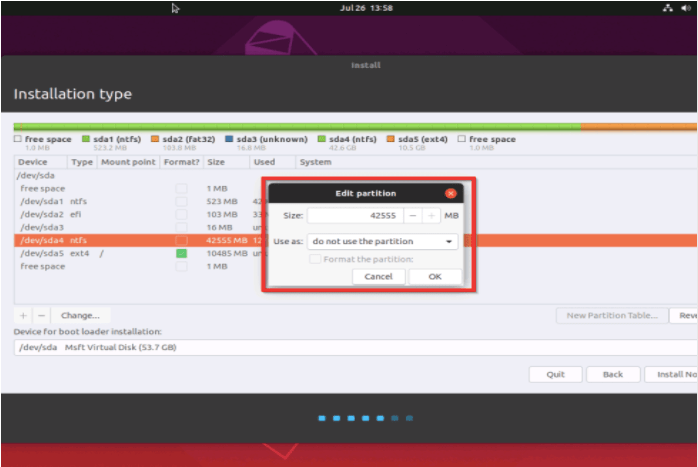
3. Once you press the file system, the image of the highlighted portion will be available, and you must press the use as a drop-down option to choose the file and then press the OK tab to complete the change.
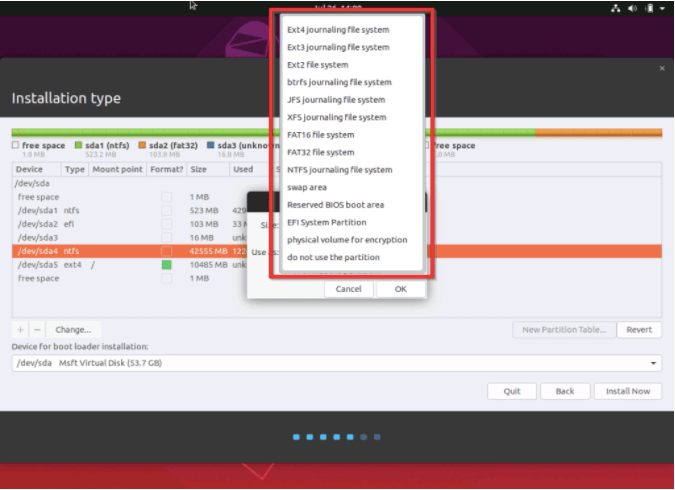
This way, once you have removed the Windows partition, you will no longer receive the ‘No root file system is defined’ error message and you can go ahead and install your Linux or Ubuntu distribution files.
3. Make a Linux partition and to it assign a root partition
Follow these steps to make the changes that you need when you get the ‘No root file system is defined error.’
1. Choose a free partition and press the + sign to add the partition.
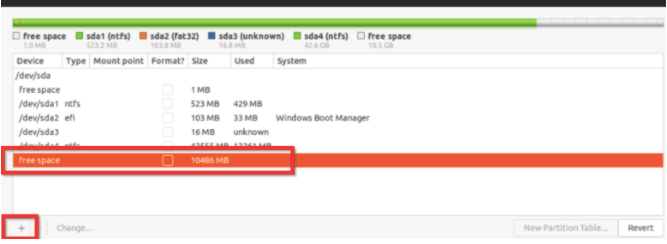
2. The create partition window opens up as soon as you load the + sign.
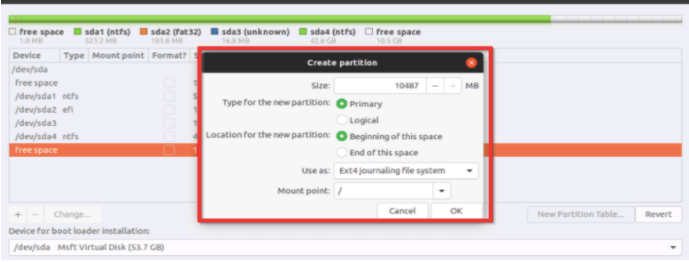
3. From the create partition window, this is how you go about;
- Add a default file size value in MB here in this segment.
- Choose from the primary or logical partition option.
- Once you have chosen the primary or the logical partition option, from the new partition location option, choose the starting or the ending of space option.
- Now, choose a file system, and you can select any from the available options.
- Further, you must select a mount point from the different mount point options.
- For enabling the root partition choose the option, /.
- Once you are done, press the OK tab to complete to remove the ‘No root file system is defined error’.
FAQs
How do you fix no root file system is defined?
Whenever you are receiving such a No root file system is defined error, you can follow the options described above to solve and rectify them. Above we have mentioned three different solutions to the problem. You can use them to eliminate the No root file system is defined error.
What is the root filesystem?
Files essential for operating the device are found in the root files system. If you mount one file above the other then the root filesystem might be the hierarchical files containing the operation files for your device, and different booting programs present within the system.
How do you create a root file system?
Building a root filesystem consists of two steps- a step where you create and another where you execute the buildrootfilesystem script.
However, each of these is split into different steps which include the process as given below;
- Decide what packages need to be downloaded.
- Create new root file directories.
- Download different packages
- Pull out the package content to a temporary directory.
- Shift the files into the new rootfilesystem directory simply by copying them to the new location.
- Remove all debugging information from the files
- Create files required for added configuration and create the /dev directory further.
- Use different preparation techniques to create the rootfilesystem into a directory.
What should be the mount point in Ubuntu?
The mount point for Ubuntu will have to contain the OS disk © and the secondary disk. You must mount your primary OS disk in “/” and the secondary one can be anywhere but automatically it is mounted to /media/your-user/your-disk-name, if that is appropriately connected.





